Hi,
I will explain Linux Commands for Beginners in this tutorial series.
In a basic sense, Linux commands are classified into 6 subjects.
- File and Directory Command
- System commands
- System statistic commands
- Process commands
- Search commands
- Network commands
- Package Installation commands
- Hardware commands
We will run all of these commands on the Terminal in Linux.
1.File and Directory Command
Basic File & Directory commands used in Linux / Unix are generally commands that allow access, deletion, modification, creation, compression, and existing files to various files and directories.
These commands are as follows.
- ls
- pwd
- cd
- mkdir
- rm
- cp
- mv
- wc
- ln
- touch
- cat
- more
- head
- tail
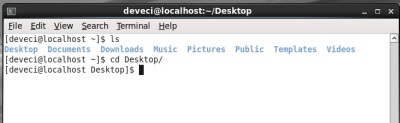
ls ( List )
This command list the existing folders or files in the current directory. Equivalent to the Dir command in Unix and Windows. The ls command returns different values according to the parameter it gets.
I will not explain all the parameters here. Just type “man ls” to see all parameters and usage.
execute ls in the current directory, output will be as follows.
If you use the ls command as ls -a, it will list all open hidden files in the directory. Or if you use ls command as ls -l, it gives extensive information about the files in the directory. It contains information about the modification date and priviliges for the file, etc.
The use and output of the command are as follows.
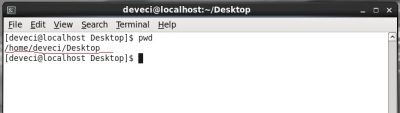
pwd ( Print Working Directory )
This command displays current working directory as follows.
[root@MehmetSalih scripts]# pwd /home/oracle/scripts [root@MehmetSalih scripts]# [root@MehmetSalih scripts]# cd .. [root@MehmetSalih oracle]# [root@MehmetSalih oracle]# pwd /home/oracle [root@MehmetSalih oracle]#
cd ( Change Directory )
This command is used to change the specified directory.
Usage of command is as follows.
cd “Directory_Name”
cd .. will take you one level up the directory.
cd ~ will take you to the top directory.
[root@MehmetSalih scripts]# pwd /home/oracle/scripts [root@MehmetSalih scripts]# [root@MehmetSalih scripts]# cd .. [root@MehmetSalih oracle]# [root@MehmetSalih oracle]# pwd /home/oracle [root@MehmetSalih oracle]# [root@MehmetSalih oracle]# cd ~ [root@MehmetSalih ~]# [root@MehmetSalih ~]# [root@MehmetSalih ~]# pwd /root [root@MehmetSalih ~]#
mkdir ( Make Directory )
The task of this command is to create a new directory with the name specified in the directory where it is located.
[root@MehmetSalih oracle]#[root@MehmetSalih oracle]# mkdir mehmet
[root@MehmetSalih oracle]#
[root@MehmetSalih oracle]# cd mehmet/
[root@MehmetSalih mehmet]#
[root@MehmetSalih mehmet]# pwd
/home/oracle/mehmet
rm ( Remove )
The file specified by this command is deleted.
You can use as rm -r “Directory Name”. The directory specified by this usage is deleted.
If you don’t want to reply rm question for remove, you can use -rf option to delete without question.
rm -rf command removes a directory along with its content forcefully and recursively.
[root@MehmetSalih oracle]# rm nohup.out rm: remove regular file `nohup.out'? y [root@MehmetSalih oracle]# [root@MehmetSalih oracle]# [root@MehmetSalih oracle]# rm -r mehmet/ rm: remove directory `mehmet'? y [root@MehmetSalih oracle]# [root@MehmetSalih oracle]# [root@MehmetSalih oracle]# rm -rf mehmet/ [root@MehmetSalih oracle]#
cp ( Copy )
With this command, the contents of a specified file or directory are copied to another specified file or directory. Its use is as follows.
You can copy a file with cp command and copy a directory and its content with cp -r command.
[root@MehmetSalih oracle]# cp controlfile.bkp Control.bck [root@MehmetSalih oracle]# [root@MehmetSalih oracle]# [root@MehmetSalih oracle]# ls -l Control.bck -rw-r----- 1 root root 127270912 Sep 9 13:55 Control.bck [root@MehmetSalih oracle]# [root@MehmetSalih oracle]# cd mehmet/ [root@MehmetSalih mehmet]# [root@MehmetSalih mehmet]# mkdir salih [root@MehmetSalih mehmet]# [root@MehmetSalih mehmet]# ls -ltr total 4 drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Sep 9 13:53 salih [root@MehmetSalih mehmet]# [root@MehmetSalih mehmet]# cd .. [root@MehmetSalih oracle]# If you try to copy directory with cp command, you will get following error. [root@MehmetSalih oracle]# cp mehmet/ MehmetSalih cp: omitting directory `mehmet/' [root@MehmetSalih oracle]# [root@MehmetSalih oracle]# You should use cp -r command for directory. [root@MehmetSalih oracle]# cp -r mehmet/ MehmetSalih [root@MehmetSalih oracle]# [root@MehmetSalih oracle]# cd MehmetSalih/ [root@MehmetSalih MehmetSalih]# [root@MehmetSalih MehmetSalih]# ls -l total 4 drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Sep 9 13:54 salih [root@MehmetSalih MehmetSalih]# [root@MehmetSalih MehmetSalih]# pwd /home/oracle/MehmetSalih [root@MehmetSalih MehmetSalih]# cd .. [root@MehmetSalih oracle]# [root@MehmetSalih oracle]#
mv ( Move )
With this command, a file can be moved to another directory or the name can be changed with this command.
Its use is as follows.
Any directory can be moved as follows.
[root@MehmetSalih mehmet]# mv salih/ ../ [root@MehmetSalih mehmet]# [root@MehmetSalih mehmet]# cd .. [root@MehmetSalih oracle]# [root@MehmetSalih oracle]# cd salih/ [root@MehmetSalih salih]# [root@MehmetSalih salih]# pwd /home/oracle/salih [root@MehmetSalih salih]#
Any directory can be renamed as follows.
[root@MehmetSalih oracle]# mv salih/ Deveci [root@MehmetSalih oracle]# [root@MehmetSalih oracle]# cd Deveci/ [root@MehmetSalih Deveci]# [root@MehmetSalih Deveci]# pwd /home/oracle/Deveci [root@MehmetSalih Deveci]# [root@MehmetSalih Deveci]#
wc ( Word Count )
This command displays the number of lines, words and characters of the specified file.
Its use is as follows.
[root@MehmetSalih oracle]# wc error.log 108840 417220 3056666 error.log -- error.log contains 108840 lines, 417220 words and 3056666 characters [root@MehmetSalih oracle]#
ln ( Link )
With this command you can call a file with a symbolic link. In other words, this link will keep the address of our file.
Its use is as follows.
You can link error.log with error like following, then you can use error.log as error.
[root@MehmetSalih oracle]# [root@MehmetSalih oracle]# ln error.log error [root@MehmetSalih oracle]# [root@MehmetSalih oracle]# [root@MehmetSalih oracle]# wc error 108840 417220 3056666 error [root@MehmetSalih oracle]# [root@MehmetSalih oracle]#
You can link any directory with ln -s command, then you can use that link instead of original directory.
[root@MehmetSalih oracle]# [root@MehmetSalih oracle]# ln -s MehmetSalih/ MSD [root@MehmetSalih oracle]# [root@MehmetSalih oracle]# [root@MehmetSalih oracle]# cd MSD/ [root@MehmetSalih MSD]# [root@MehmetSalih MSD]# [root@MehmetSalih MSD]# pwd /home/oracle/MSD [root@MehmetSalih MSD]# [root@MehmetSalih MSD]# [root@MehmetSalih MSD]# mkdir deveci [root@MehmetSalih MSD]# [root@MehmetSalih MSD]# [root@MehmetSalih MSD]# ls -ltr total 8 drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Sep 9 13:54 salih drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Sep 9 14:18 deveci [root@MehmetSalih MSD]# Content of MSD is actually content of MehmetSalih, MSD is just link of MehmetSalih directory. [root@MehmetSalih MSD]# cd ../MehmetSalih/ [root@MehmetSalih MehmetSalih]# [root@MehmetSalih MehmetSalih]# [root@MehmetSalih MehmetSalih]# ls -ltr total 8 drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Sep 9 13:54 salih drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Sep 9 14:18 deveci [root@MehmetSalih MehmetSalih]#
touch
This command creates a file with 0 bytes size with the current date if it does not exist. Use of the command is as follows.
[root@MehmetSalih oracle]#
[root@MehmetSalih oracle]# touch MehmetDeveci
[root@MehmetSalih oracle]#
[root@MehmetSalih oracle]#
[root@MehmetSalih oracle]# ls -l MehmetDeveci
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Sep 9 14:23 MehmetDeveci
[root@MehmetSalih oracle]#
cat ( Concatenate )
The contents of the file specified by this command are displayed. Usage of command is as follows.
[root@MehmetSalih oracle]# cat MehmetDeveci State : Optimal Strip Size : 1.0 MB Number Of Drives : 4 Span Depth : 1 Is VD Cached: No Exit Code: 0x00 [root@MehmetSalih oracle]#
You can use cat> File1 usage, thus you can Insert data from standard input to file1. When you execute this command, the standard input waits for data, and after you complete the data you typed, you can finish the standard input with ctrl-c. The data you entered is saved with File1. With this command, the contents of File1 are reset first and then the data you enter is added.
If you want to add data from the standard input to the existing data, use the following usage.
cat >> File1 adds and saves the data from the standard input from the EndofFile of File1.
[root@urfadbadm01 oracle]# cat >>MehmetDeveci Hi, I am Mehmet Salih Deveci ^C [root@urfadbadm01 oracle]# [root@MehmetSalih oracle]# cat MehmetDeveci State : Optimal Strip Size : 1.0 MB Number Of Drives : 4 Span Depth : 1 Is VD Cached: No Exit Code: 0x00 Hi, I am Mehmet Salih Deveci [root@MehmetSalih oracle]# [root@MehmetSalih oracle]# cat >MehmetDeveci Hi, I am Mehmet Salih Deveci ^C [root@MehmetSalih oracle]# [root@MehmetSalih oracle]# [root@MehmetSalih oracle]# cat MehmetDeveci Hi, I am Mehmet Salih Deveci [root@MehmetSalih oracle]#
more
With the help of this command, the contents of the specified file are displayed by page.
Cat command displays all content, but more command displays content of file page by page.
[root@MehmetSalih oracle]# more error.log Adapter #0 Enclosure Device ID: 252 Slot Number: 0 Drive's postion: DiskGroup: 0, Span: 0, Arm: 0 Enclosure position: 0
head
This command displays the contents of the file as in the more command, but only the first 10 lines. Its use is as follows.
[root@MehmetSalih oracle]# [root@MehmetSalih oracle]# head error.log Adapter #0 Enclosure Device ID: 252 Slot Number: 0 Drive's postion: DiskGroup: 0, Span: 0, Arm: 0 Enclosure position: 0 Device Id: 8 WWN: 51340CCA06F1980A3 Sequence Number: 2 Media Error Count: 0 [root@MehmetSalih oracle]#
tail
This command displays the contents of the file as in the more command, but only the last 10 lines. Its use is as follows.
[root@MehmetSalih oracle]# tail error.log Disk Cache Policy : Disabled Encryption Type : None Bad Blocks Exist: No PI type: No PI Is VD Cached: No Exit Code: 0x00 [root@MehmetSalih oracle]#
If you want to see more lines than 10 and keep printing new lines, you can use tail -Nf command.
I have used 15 lines in this example, If you want to change it, you can see more than 15 lines.
[root@MehmetSalih oracle]# tail -15f error.log Creation Time : 03:00:06 PM Default Cache Policy: WriteBack, ReadAheadNone, Direct, No Write Cache if Bad BBU Current Cache Policy: WriteBack, ReadAheadNone, Direct, No Write Cache if Bad BBU Default Access Policy: Read/Write Current Access Policy: Read/Write Disk Cache Policy : Disabled Encryption Type : None Bad Blocks Exist: No PI type: No PI Is VD Cached: No Exit Code: 0x00
I will continue to explain Linux commands tutorial series in the next article.
Do you want to learn Linux System Administration for Beginners, then read the following articles.
https://ittutorial.org/linux-administration-tutorial-for-beginners/
 IT Tutorial IT Tutorial | Oracle DBA | SQL Server, Goldengate, Exadata, Big Data, Data ScienceTutorial
IT Tutorial IT Tutorial | Oracle DBA | SQL Server, Goldengate, Exadata, Big Data, Data ScienceTutorial