Hi,
I will continue to explain Linux Commands for Beginners in this tutorial series.
You can read first article before this.
GNU/Linux Bash Commands Tutorial for Beginners -1 Working with Files and Directories
2. System commands
System commands in Linux are generally used to learn about time, calendar, cpu, disk and memory, or other necessary information about the system.
These commands are as follows.
- date
- cal
- uptime
- whereis
- which
- uname
- w
- whoami
- cat /proc/cpuinfo
- cat /proc/meminfo
date
With this command, you can display the current time and date of the system. Its use is as follows.
[root@MehmetSalih ~]#
[root@MehmetSalih ~]# date
Tue Sep 10 16:29:44 +03 2019
[root@MehmetSalih ~]#
cal
With this command, the system displays the current month as a 1-month calendar. This command can also take parameters. If you want to see a month of any year, you should type a command like the one below.
[root@MehmetSalih ~]# cal
September 2019
Su Mo Tu We Th Fr Sa
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
8 9 10 11 12 13 14
15 16 17 18 19 20 21
22 23 24 25 26 27 28
29 30
[root@MehmetSalih ~]#
[root@MehmetSalih ~]# cal 5 1989
May 1989
Su Mo Tu We Th Fr Sa
1 2 3 4 5 6
7 8 9 10 11 12 13
14 15 16 17 18 19 20
21 22 23 24 25 26 27
28 29 30 31
[root@MehmetSalih ~]#
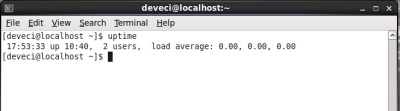
uptime
This command is used to display how long the machine has been running continuously. This command returns the user the current time, how long it has been running, the number of active users in the system, and the load performance of the system in the last minutes.
Usage and output are as follows.
[root@MehmetSalih ~]# uptime 16:29:54 up 1 day, 2:48, 5 users, load average: 0.05, 0.07, 0.11 [root@MehmetSalih ~]#
whereis
The executable file for a given file or command with this command indicates the location of the executable file or source files on the server.
Use of the command is as follows.
[root@MehmetSalih oradata]# whereis date date: /bin/date /usr/share/man/man1/date.1.gz /usr/share/man/man1p/date.1p.gz [root@MehmetSalih oradata]#
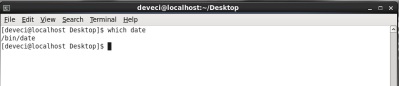
which
Gives the full path of Linux command on the server. Its use is as follows.
[root@MehmetSalih oradata]# which date /bin/date [root@MehmetSalih oradata]#
uname
With this command, the parameter to be entered as -a gives various information about the system such as your machine type, network host name and so on. usage and examples are as follows.
[root@MehmetSalih ~]# uname Linux [root@MehmetSalih ~]# [root@MehmetSalih ~]# [root@MehmetSalih ~]# uname -a Linux MehmetSalih 3.8.13-118.13.3.el6uek.x86_64 #2 SMP Fri Oct 21 14:30:26 PDT 2016 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/Linux [root@MehmetSalih ~]# [root@MehmetSalih ~]# [root@MehmetSalih ~]# uname -i x86_64 [root@MehmetSalih ~]#
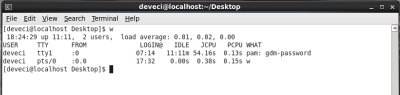
w
With this command, user can see who is active in the system and what he or she is doing. Its use is as follows.
whoami
With this command, the user who is currently logged in the system is displayed.
[root@MehmetSalih ~]# whoami root [root@MehmetSalih ~]# su - oracle [oracle@MehmetSalih ~]$ [oracle@MehmetSalih ~]$ whoami oracle [oracle@MehmetSalih ~]$
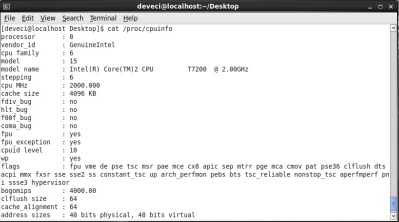
cat /proc/cpuinfo
This command provides the user with detailed information about the CPU. Use of the command is as follows.
Bu komut ile sistemi yöneten merkezi işlem birimi (Cpu) nin çalışması hakkında ayrıntılı bilgi kullanıcıya sunulur. Komutun kullanımı aşağıdaki gibidir.
[root@MehmetSalih ~]# cat /proc/cpuinfo
processor : 0
vendor_id : GenuineIntel
cpu family : 6
model : 63
model name : Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU E5-2680 v3 @ 2.50GHz
stepping : 2
microcode : 0x39
cpu MHz : 2499.998
cache size : 30720 KB
physical id : 0
siblings : 4
core id : 0
cpu cores : 4
apicid : 0
initial apicid : 0
fpu : yes
fpu_exception : yes
cpuid level : 13
wp : yes
flags : fpu vme de pse tsc msr pae mce cx8 apic sep mtrr pge mca cmov pat pse36 clflush dts mmx fxsr sse sse2 ss ht syscall nx pdpe1gb rdtscp lm constant_tsc arch_perfmon pebs bts nopl xtopology tsc_reliable nonstop_tsc eagerfpu pni pclmulqdq ssse3 fma cx16 pcid sse4_1 sse4_2 x2apic movbe popcnt tsc_deadline_timer aes xsave avx f16c rdrand hypervisor lahf_lm abm arat xsaveopt fsgsbase tsc_adjust bmi1 avx2 smep bmi2 invpcid
bogomips : 4999.99
clflush size : 64
cache_alignment : 64
address sizes : 42 bits physical, 48 bits virtual
power management:
processor : 1
vendor_id : GenuineIntel
.......................
....................
processor : 15
vendor_id : GenuineIntel
cpu family : 6
model : 63
model name : Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU E5-2680 v3 @ 2.50GHz
stepping : 2
microcode : 0x39
cpu MHz : 2499.998
cache size : 30720 KB
physical id : 3
siblings : 4
core id : 3
cpu cores : 4
apicid : 15
initial apicid : 15
fpu : yes
fpu_exception : yes
cpuid level : 13
wp : yes
flags : fpu vme de pse tsc msr pae mce cx8 apic sep mtrr pge mca cmov pat pse36 clflush dts mmx fxsr sse sse2 ss ht syscall nx pdpe1gb rdtscp lm constant_tsc arch_perfmon pebs bts nopl xtopology tsc_reliable nonstop_tsc eagerfpu pni pclmulqdq ssse3 fma cx16 pcid sse4_1 sse4_2 x2apic movbe popcnt tsc_deadline_timer aes xsave avx f16c rdrand hypervisor lahf_lm abm arat xsaveopt fsgsbase tsc_adjust bmi1 avx2 smep bmi2 invpcid
bogomips : 4999.99
clflush size : 64
cache_alignment : 64
address sizes : 42 bits physical, 48 bits virtual
power management:
[root@MehmetSalih ~]#
cat /proc/meminfo
This command provides detailed information about the operation of RAM (Random Access Memory) in the server. Use of the command is as follows.
[root@MehmetSalih ~]# cat /proc/meminfo MemTotal: 49463392 kB MemFree: 171816 kB Buffers: 331572 kB Cached: 46352256 kB SwapCached: 27664 kB Active: 39452124 kB Inactive: 8347072 kB Active(anon): 39098508 kB Inactive(anon): 7994460 kB Active(file): 353616 kB Inactive(file): 352612 kB Unevictable: 0 kB Mlocked: 0 kB SwapTotal: 4194300 kB SwapFree: 1433652 kB Dirty: 492 kB Writeback: 0 kB AnonPages: 1091212 kB Mapped: 26328108 kB Shmem: 45977576 kB Slab: 739528 kB SReclaimable: 605408 kB SUnreclaim: 134120 kB KernelStack: 6152 kB PageTables: 377244 kB NFS_Unstable: 0 kB Bounce: 0 kB WritebackTmp: 0 kB CommitLimit: 28925996 kB Committed_AS: 89343800 kB VmallocTotal: 34359738367 kB VmallocUsed: 247156 kB VmallocChunk: 34333911692 kB HardwareCorrupted: 0 kB HugePages_Total: 0 HugePages_Free: 0 HugePages_Rsvd: 0 HugePages_Surp: 0 Hugepagesize: 2048 kB DirectMap4k: 14208 kB DirectMap2M: 3131392 kB DirectMap1G: 49283072 kB [root@MehmetSalih ~]#
I will continue to explain Linux commands tutorial series in the next article.
 IT Tutorial IT Tutorial | Oracle DBA | SQL Server, Goldengate, Exadata, Big Data, Data ScienceTutorial
IT Tutorial IT Tutorial | Oracle DBA | SQL Server, Goldengate, Exadata, Big Data, Data ScienceTutorial