Hi
I will continue to explain Storage Server Disk operations in the Oracle Exadata in this article.

Read previous articles before this article.
The file system structure on Storage Cell is as follows. Let’s see what each partition does.

- The /dev/md5 and /dev/md6 system partitions are root partitions containing the OS image.
- /dev/md6 and /dev/md8 include the exadata software.
- Includes /dev/md4 boot image
- /dev/md11 keeps crash and log files
You can mount any cell max 4 md partition.
Each physical disk in Exadata is generally used as follows. The most inner part of physical partition is OS or DBFS partition and then RECO Partitions come, and outermost part of LUN is used for DATA like following.

These 12 physical disks can be mapped to the Storage server as 12 LUNs and then used as a Cell disk in the Cell (Storage) server. The following image summarizes this structure very well.
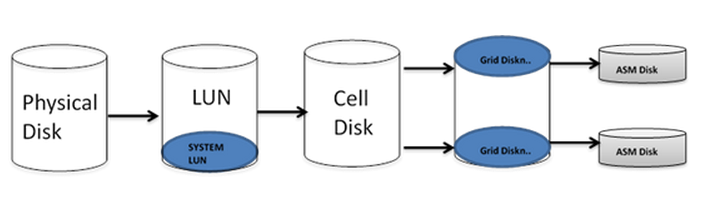
Essentially, Physical Disks are the original disks on the Storage ( Cell ) Server and these are mapped to the Cell Server. Each Cell Disk is created from these LUNs. Each Cell disk can be divided or partitioned into one or more Grid Disks.
Each Grid disk is suitable for use in the ASM Disk group. This configuration is done during the installation of the first Exadata machine. Then, as I will do in the examples, these configurations can be changed upon request or after any physical disk problem.
To understand the Physical Disk, Lun, Cell Disk, and Grid disk between each other ,I will give an example like following.
On each Cell Server, there are 12 Physical Disks and 12 LUNs like following. Flash disks and LUNs will be described later.

This 12 physical disks corresponds to 12 LUNs and 12 Cell Disks in the Cell Server as seen below.

In response to 12 Cell disks, as I mentioned above, it can be divided into more than one Grid disk. Each Cell Disk is divided into 36 Grid Disk or more.

These 36 Grid Disks are referred to ASM (Automatic Storage Management) directly as ASM Disks. You can create a disk group with each ASM disk (Grid Disk) or you can add this disk to an existing disk group.
Do you want to learn Exadata detailed, then read the following articles.
https://ittutorial.org/exadata-tutorials-oracle-magic-database-machine-exadata-lessons/
 IT Tutorial IT Tutorial | Oracle DBA | SQL Server, Goldengate, Exadata, Big Data, Data ScienceTutorial
IT Tutorial IT Tutorial | Oracle DBA | SQL Server, Goldengate, Exadata, Big Data, Data ScienceTutorial