Hi ,
In this article , I will tell you how to use the default value , how to copy data from another table .
USING DEFAULT VALUE
The default value specified for the table column is assigned . It tries to prevent users from entering incorrectly and can be used in Insert and Update . Here’s an example of using the default value :
INSERT INTO ADMIN.NEW_TABLE(EMPLOYEE_ID,FIRST_NAME,LAST_NAME) VALUES (12,'Marlyn',DEFAULT);
SELECT * FROM ADMIN.NEW_TABLE WHERE EMPLOYEE_ID=12;
![]()
In our current example we create a table and we will add columns such as name and surname to this table , then we will make a default column that we have chosen so that if we don’t add anything to that column , we will return the default value . You will understand more easily when you look at the pictures below 🙂
CREATE TABLE TEST1 ( ISIM VARCHAR2(20), SOYISIM VARCHAR2(20) DEFAULT 'Duran', TARIH DATE )
Here we created our table and set our default value .
INSERT INTO TEST1 VALUES('Melike',DEFAULT,SYSDATE);Now we have added to our table above .
SELECT * FROM TEST1;
And the result :

COPYING DATA FROM ANY OTHER TABLE
With insert we can copy data from one table to another table using subqueries . But Values are not used here . The number of columns in the insert statement and the number of columns in the subquery must be the same .
When we say WHERE 1 = 0 , we only get the structure of the table , not the data .
CREATE TABLE NEW_TEST AS SELECT EMPLOYEE_ID,LAST_NAME,HIRE_DATE,JOB_ID,SALARY FROM ADMIN.NEW_TABLE WHERE 1=0;
As you can see above , we created a new table and when we created this table , we took the structure of admin.new_table table .
INSERT INTO NEW_TEST SELECT EMPLOYEE_ID,LAST_NAME,HIRE_DATE,JOB_ID,SALARY FROM ADMIN.NEW_TABLE WHERE EMPLOYEE_ID=6;
Now , we have added the person whose employee_id is equal to 6 to the table we created.
SELECT * FROM NEW_TEST;
![]()
MULTI INSERT
We’ve seen just inserting data into our table with the Insert statement , and now we’ll see how to add records to multiple tables at the same time with an insert clause under this topic .
Multiple inserts are widely used in DataWarehouse systems . We can provide Conditional Insert using IF – THEN . Use of :
INSERT ALL INTO target_a VALUES ( ... , .....) INTO target_b VALUES ( ... , .....) INTO target_c VALUES ( ... , .....) SELECT ....... FROM sourcetab WHERE ....... ;
WHAT ARE THE MULTIPLE INSERT TYPES ?
UNDERSTANDING INSERT
CONDITIONAL INSERT ALL
CONDITIONAL INSERT FIRST
VERTICAL INSERT
UNDERSTANDING INSERT ALL
Now let’s create 2 tables from admin.new_table table and add the person named marlyn to these tables at the same time :
CREATE TABLE BOLUM_TEST AS SELECT * FROM ADMIN.NEW_TABLE WHERE 1=0;
CREATE TABLE BOLUM_TEST2 AS SELECT * FROM ADMIN.NEW_TABLE WHERE 1=0;
Now we have created our tables with conditional insert all , we want to add marlyn to both tables at the same time :
INSERT ALL INTO BOLUM_TEST VALUES(EMPLOYEE_ID,FIRST_NAME,LAST_NAME,HIRE-DATE,JOB_ID,SALARY) INTO BOLUM_TEST2 VALUES(EMPLOYEE_ID,FIRST_NAME,LAST_NAME,HIRE-DATE,JOB_ID,SALARY) SELECT EMPLOYEE_ID,FIRST_NAME,LAST_NAME,HIRE_DATE,JOB_ID,SALARY FROM ADMIN.NEW_TABLE WHERE FIRST_NAME='Marlyn'; SELECT * FROM BOLUM_TEST2;
And we’re checking to see if it was last added :
![]()
CONDITIONAL INSERT ALL
INSERT ALL WHEN EMPLOYEE_ID>4 THEN INTO BOLUM_TEST VALUES(EMPLOYEE_ID,FIRST_NAME,LAST_NAME,HIRE_DATE,JOB_ID,SALARY) WHEN FIRST_NAME IS NOT NULL THEN INTO BOLUM_TEST2 VALUES(EMPLOYEE_ID,FIRST_NAME,LAST_NAME,HIRE_DATE,JOB_ID,SALARY) SELECT EMPLOYEE_ID,FIRST_NAME,LAST_NAME,HIRE_DATE,JOB_ID,SALARY FROM ADMIN.NEW_TABLE;
SELECT * FROM BOLUM_TEST;

SELECT * FROM BOLUM_TEST2;
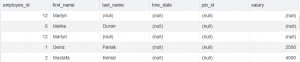
CONDITIONAL INSERT FIRST
Now let’s create 3 experiment tables to understand this topic .
CREATE TABLE SALARY_HIGH AS SELECT EMPLOYEE_ID,FIRST_NAME,LAST_NAME,HIRE_DATE,JOB_ID,SALARY FROM ADMIN.NEW_TABLE WHERE 1=0;
CREATE TABLE SALARY_LOW AS SELECT EMPLOYEE_ID,FIRST_NAME,LAST_NAME,HIRE_DATE,JOB_ID,SALARY FROM ADMIN.NEW_TABLE WHERE 1=0;
CREATE TABLE SALARY_MIDDLE AS SELECT EMPLOYEE_ID,FIRST_NAME,LAST_NAME,HIRE_DATE,JOB_ID,SALARY FROM ADMIN.NEW_TABLE WHERE 1=0;
Let’s insert the new_table table at the same time . In doing so , according to the salary , let’s insert it into 3 .
INSERT FIRST WHEN SALARY < 4500 THEN INTO SALARY_LOW VALUES(EMPLOYEE_ID,FIRST_NAME,LAST_NAME,HIRE_DATE,JOB_ID,SALARY) WHEN SALARY BETWEEN 4500 AND 7000 THEN INTO SALARY_MIDDLE VALUES(EMPLOYEE_ID,FIRST_NAME,LAST_NAME,HIRE_DATE,JOB_ID,SALARY) ELSE INTO SALARY_HIGH VALUES(EMPLOYEE_ID,FIRST_NAME,LAST_NAME,HIRE_DATE,JOB_ID,SALARY) SELECT EMPLOYEE_ID,FIRST_NAME,LAST_NAME,HIRE_DATE,JOB_ID,SALARY FROM ADMIN.NEW_TABLE;
Now let’s list the highest salary areas :
SELECT * FROM SALARY_HIGH;
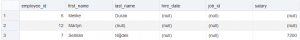
Now the areas between the two salary values are :
SELECT * FROM SALARY_MIDDLE;
![]()
And finally, to see salaries below 4500 :
SELECT * FROM SALARY_LOW;
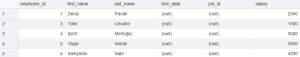
VERTICAL INSERT
Let’s create a table named SALES_SOURCE .
CREATE TABLE SALES_SOURCE( EMPNO NUMBER(5), SALES_M NUMBER(8,2), SALES_TU NUMBER(8,2), SALES_W NUMBER(8,2), SALES_TH NUMBER(8,2), SALES_F NUMBER(8,2));
And create a table named SALES_INFO .
CREATE TABLE SALES_INFO( EMPID NUMBER(6), WEEK NUMBER(2), SALES NUMBER(8,2));
Now add to the SALES_SOURCE table :
INSERT INTO SALES_SOURCE VALUES(180,1000,2000,3000,4000,5000);
Let’s insert the data of sales_source table into the sales_info table by making vertical insert :
INSERT ALL INTO SALES_INFO VALUES(EMPNO,WEEKID,SALES_M) INTO SALES_INFO VALUES(EMPNO,WEEKID,SALES_TU) INTO SALES_INFO VALUES(EMPNO,WEEKID,SALES_W) INTO SALES_INFO VALUES(EMPNO,WEEKID,SALES_TH) INTO SALES_INFO VALUES(EMPNO,WEEKID,SALES_F) SELECT EMPNO,WEEKID,SALES_M,SALES_TU,SALES_W,SALES_TH,SALES_F FROM SALES_SOURCE;
We check the sales_info table to check :
SELECT * FROM SALES_INFO;
MERGE
Provides conditional execution of insert , update, delete operations in a table . If the corresponding row is present in the table , update becomes insert . Used in DataWirehouse applications . And it saves us from updating separately .
Create a merge_test table from the NEW_TABLE table .
CREATE TABLE MERGE_TEST AS SELECT * FROM ADMIN.NEW_TABLE WHERE 1=0;
MERGE INTO MERGE_TEST c USING(SELECT * FROM ADMIN.NEW_TABLE) e ON(c.EMPLOYEE_ID=e.EMPLOYEE_ID) WHEN MATCHED THEN UPDATE SET c.FIRST_NAME=e.FIRST_NAME, c.LAST_NAME=e.LAST_NAME WHEN NOT MATCHED THEN INSERT VALUES(e.EMPLOYEE_ID,e.FIRST_NAME,e.LAST_NAME,e.HIRE_DATE,e.SALARY);
And finally we run the following query to see the merge_test table .
SELECT * FROM MERGE_TEST;
We will see that the records in the new_table table are added to the merge_test table .

See you in my next post.
 IT Tutorial IT Tutorial | Oracle DBA | SQL Server, Goldengate, Exadata, Big Data, Data ScienceTutorial
IT Tutorial IT Tutorial | Oracle DBA | SQL Server, Goldengate, Exadata, Big Data, Data ScienceTutorial