Hi ,
In this article I will tell you the differences between time expressions and how they are used .
TIMEZONE PARAMETER
How TIME_ZONE is updated :
By giving the region name ,
By giving full time ,
By giving the operating system time zone ,
Time zone of the database .
ALTER SESSION SET TIME_ZONE= ‘+03:00’; ALTER SESSION SET TIME_ZONE=dbtimezone; ALTER SESSION SET TIME_ZONE=local; ALTER SESSION SET TIME_ZONE= ‘TURKEY’;
PRESENT TENSE
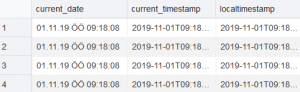
CURRENT_DATE : Returns the current date in the user session and is of DATE type .
CURRENT_TIMESTAMP : Returns the current time and date in the user session . TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE (timezone_hour , timezone_minute) .
LOCAL_TIMESTAMP : Returns the current date and time . Timestamp (year , month , day , minute , second) type .
Now let’s make an example to reinforce what we have written above :
SELECT CURRENT_DATE,CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,LOCALTIMESTAMP FROM ADMIN.NEW_TABLE;

ALTER SESSION SET TIME_ZONE='+03:00';
![]()
SELECT DBTIMEZONE,SESSIONTIMEZONE FROM ADMIN.NEW_TABLE;

DATE AND TIMESTAMP DIFFERENCE
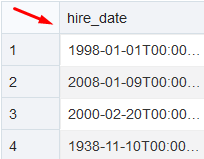
SELECT HIRE_DATE FROM ADMIN.NEW_TABLE;

ALTER TABLE ADMIN.NEW_TABLE MODIFY HIRE_DATE TIMESTAMP;
TIMESTAMP COMPARISON
Now we create a date table and use different timestamps to compare them :
CREATE TABLE TARIH( TARIH1 TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE, TARIH2 TIMESTAMP WITH LOCAL TIME ZONE);
INSERT INTO TARIH VALUES(CURRENT_DATE,CURRENT_TIMESTAMP+2);
SELECT * FROM TARIH;

INTERVAL DATA TYPES
Interval data types are used to either store the differences between the data in the two datetime types , or to add or subtract time to the data .
INTERVAL YEAR TO MONTH —> Year and month
INTERVAL DAY TO SECOND —> Day , hour , minute , second
They are divided into two .
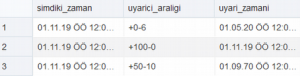
INTERVAL YEAR TO MONTH EXAMPLE :
CREATE TABLE UYARICI( UYARICI_ID NUMBER, UYARICI_ARALIGI INTERVAL YEAR(3) TO MONTH);
INSERT INTO UYARICI VALUES(1633,INTERVAL '6'MONTH);
INSERT INTO UYARICI VALUES(1854,INTERVAL'100'YEAR(3));
INSERT INTO UYARICI VALUES(8904,'50-10');
SELECT TRUNC(SYSDATE)SIMDIKI_ZAMAN,UYARICI_ARALIGI,TRUNC(SYSDATE+UYARICI_ARALIGI) UYARI_ZAMANI FROM UYARICI;
INTERVAL DAY TO SECOND EXAMPLE :
CREATE TABLE SURE_ASIMI( SURE_ID NUMBER, SURE_ARALIGI INTERVAL DAY(2) TO SECOND);
INSERT INTO SURE_ASIMI VALUES(49876,'90 00:00:00');
INSERT INTO SURE_ASIMI VALUES(78655,INTERVAL '6 03:30:16' DAY TO SECOND);
SELECT SYSDATE,SURE_ARALIGI,(SYSDATE+SURE_ARALIGI)SURE_ZAMANI FROM SURE_ASIMI;

EXTRACT
Allows to allocate some time periods of data of datetime type .
SELECT FIRST_NAME,LAST_NAME,HIRE_DATE, EXTRACT(MONTH FROM HIRE_DATE)AY, EXTRACT(YEARFROM HIRE_DATE)YIL, EXTRACT(DAY FROM HIRE_DATE)GUN FROM ADMIN.NEW_TABLE;

As you can see in the example above , we have listed the hire_date column separately as day , month , year using extract .
TZ_OFFSET
It is the expression that allows to show time zones .
SELECT TZ_OFFSET('US/EASTERN'),
TZ_OFFSET('CANADA/YUKON'),
TZ_OFFSET('EUROPE/LONDON') FROM ADMIN.NEW_TABLE;
TO_YMINTERVAL
It allows us to shift dates by giving year and month offset .
SELECT HIRE_DATE,HIRE_DATE+TO_YMINTERVAL('01-02') AS HIRE_DATE_YMINTERVAL FROM ADMIN.NEW_TABLE;
TO_DSINTERVAL
It allows us to shift dates by giving offset of day , hour , minute and second .
SELECT LAST_NAME,TO_CHAR(HIRE_DATE,'dd-mm-yy :hh:mi:ss')HIRE_DATE,TO_CHAR(HIRE_DATE+TO_DSINTERVAL('100 10:00:00'), 'dd-mm-yy:hh:mi:ss')HIREDATE_OFFSET FROM ADMIN.NEW_TABLE;
See you in my next post.
 IT Tutorial IT Tutorial | Oracle DBA | SQL Server, Goldengate, Exadata, Big Data, Data ScienceTutorial
IT Tutorial IT Tutorial | Oracle DBA | SQL Server, Goldengate, Exadata, Big Data, Data ScienceTutorial