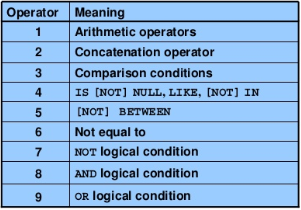
OPERATOR PRECEDENCE
- Let’s list the employees which JOB_ID is SA_REP or AD_PRES , and have salary more than 15000.
SELECT first_name,last_name, job_id, salary FROM hr.employees WHERE job_id = 'SA_REP‘ OR job_id = 'AD_PRES‘ AND salary > 15000;

This way, all employess which JOB_ID is SA_REP listed as result. We need to add parenthesis to correct this querry ;
SELECT first_name,last_name, job_id, salary FROM hr.employees WHERE (job_id = 'SA_REP‘ OR job_id = 'AD_PRES‘) AND salary > 15000;

ORDER BY OPERATOR
- The ORDER BY operator is used to put in order the data that returned from querry.
- ASC : Sorts the data in ascending direction.
- DESC : Sorts the data in descending direction.
- The default sorting is ASC. If you don’t write any or them, the data will be sorted in ascending direction.
- Let’s list the employees by the hir_date in ascending direction, older to newer.
SELECT first_name,last_name, job_id, department_id, hire_date "Hire Date“ FROM hr.employees ORDER BY hire_date ASC ;

- Let’s find the yearly salary of employees and list them by the salary in descending direction.
SELECT employee_id, first_name,last_name, salary*12 "Yearly Salary“ FROM hr.employees ORDER BY 4 desc ;

ASSIGNING VARIABLE
- Let’s list the employees which Department ID is 90, using variable.
SELECT employee_id, last_name, salary, department_id FROM hr.employees WHERE department_id = &department_num ;


 IT Tutorial IT Tutorial | Oracle DBA | SQL Server, Goldengate, Exadata, Big Data, Data ScienceTutorial
IT Tutorial IT Tutorial | Oracle DBA | SQL Server, Goldengate, Exadata, Big Data, Data ScienceTutorial
thank you for sharing with us, I think this website really stands out : D.